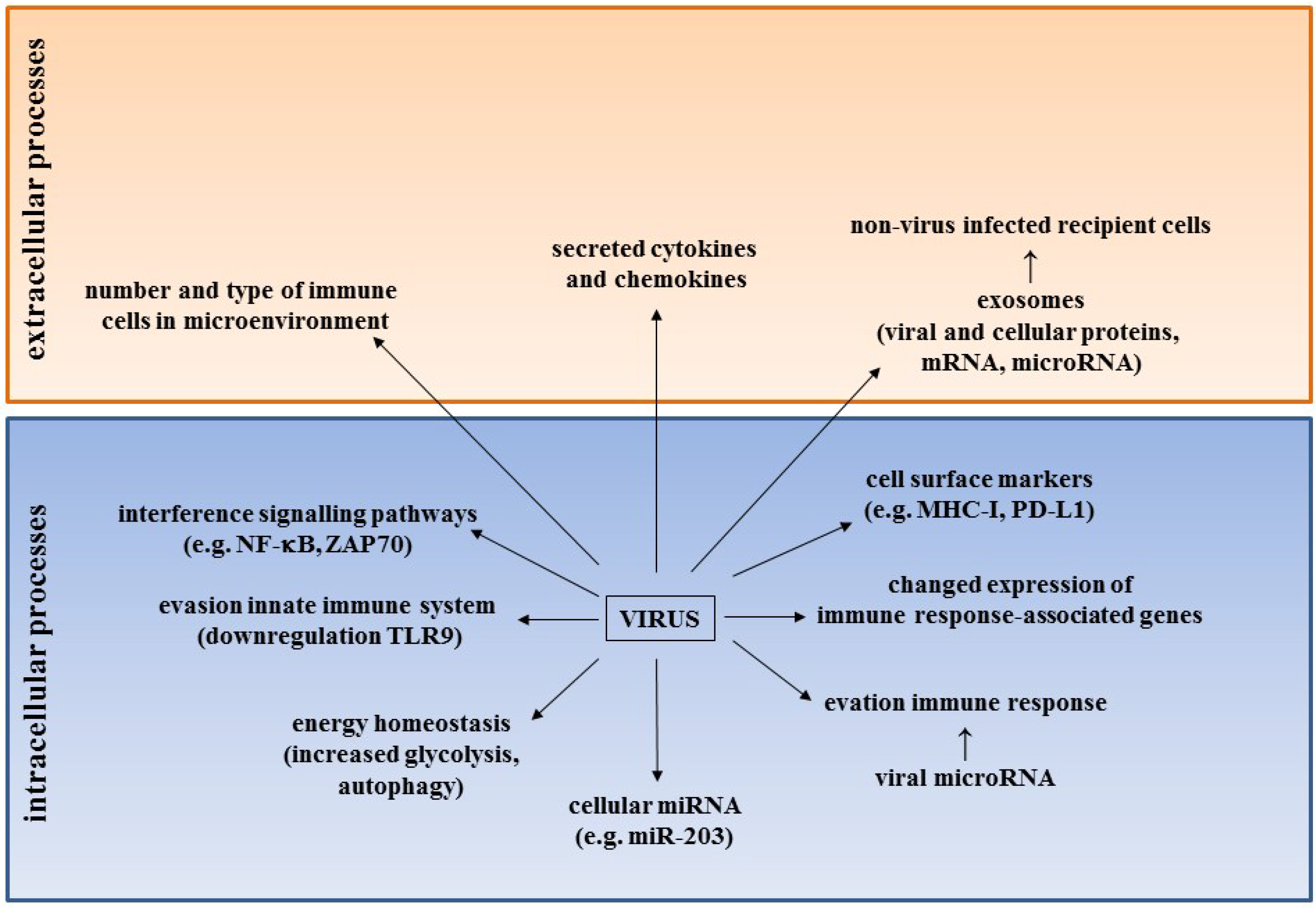
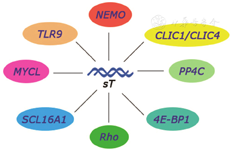
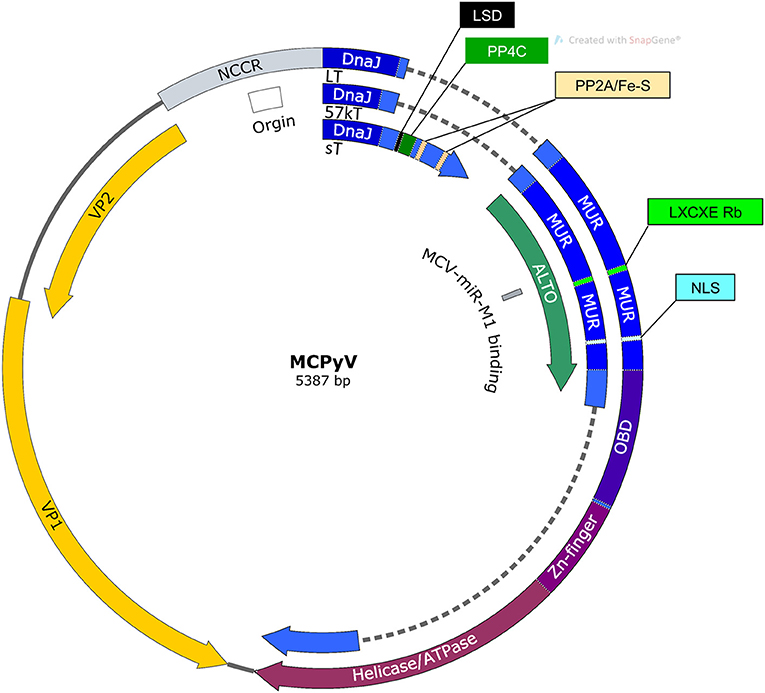
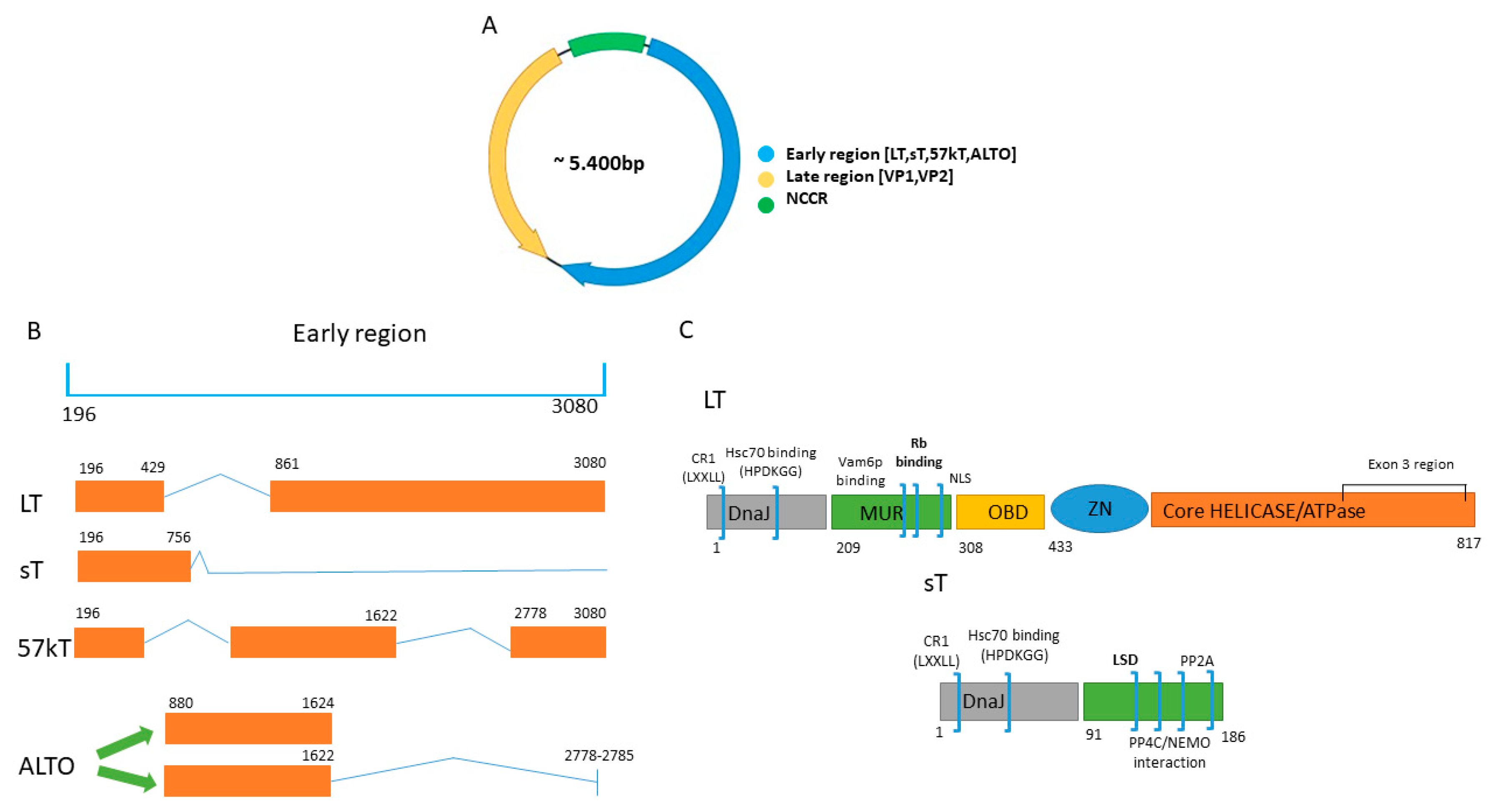
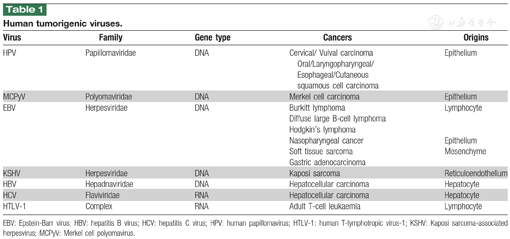
Cellular sheddases are induced by Merkel cell polyomavirus small tumour antigen to mediate cell dissociation and invasiveness | PLOS Pathogens

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Beta Human Papillomavirus and Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Skin Neoplasms | International Journal of Dermatology and Venereology

NF-κB members and NF-κB signaling. The NF-κB family is composed of five... | Download Scientific Diagram

Human Polyomaviruses: The Battle of Large and Small Tumor Antigens - Camila Freze Baez, Rafael Brandão Varella, Sonia Villani, Serena Delbue, 2017

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection Induces an Antiviral Innate Immune Response in Human Dermal Fibroblasts | Journal of Virology

Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen targets the NEMO adaptor protein to disrupt inflammatory signaling. - Abstract - Europe PMC
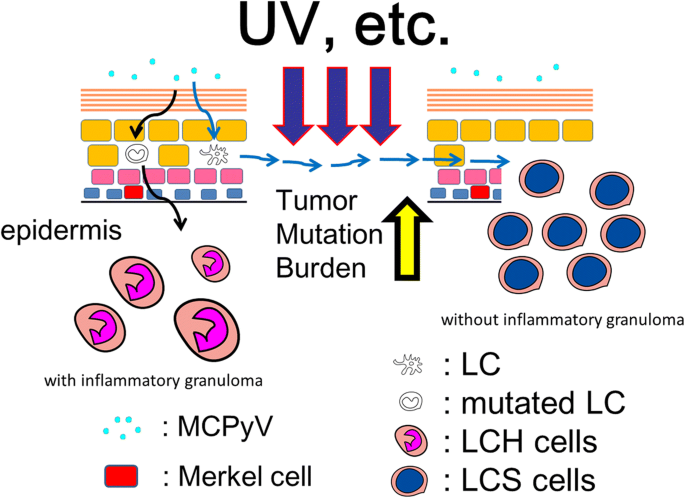
Merkel cell polyomavirus and Langerhans cell neoplasm | Cell Communication and Signaling | Full Text
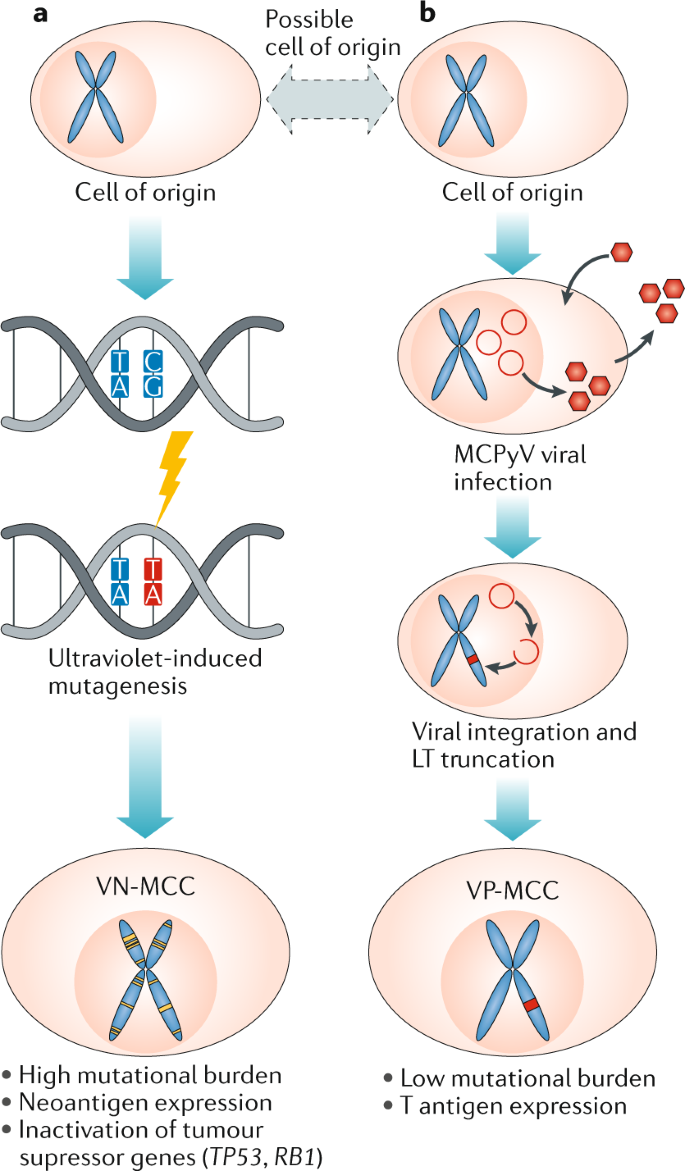
The biology and treatment of Merkel cell carcinoma: current understanding and research priorities | Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology
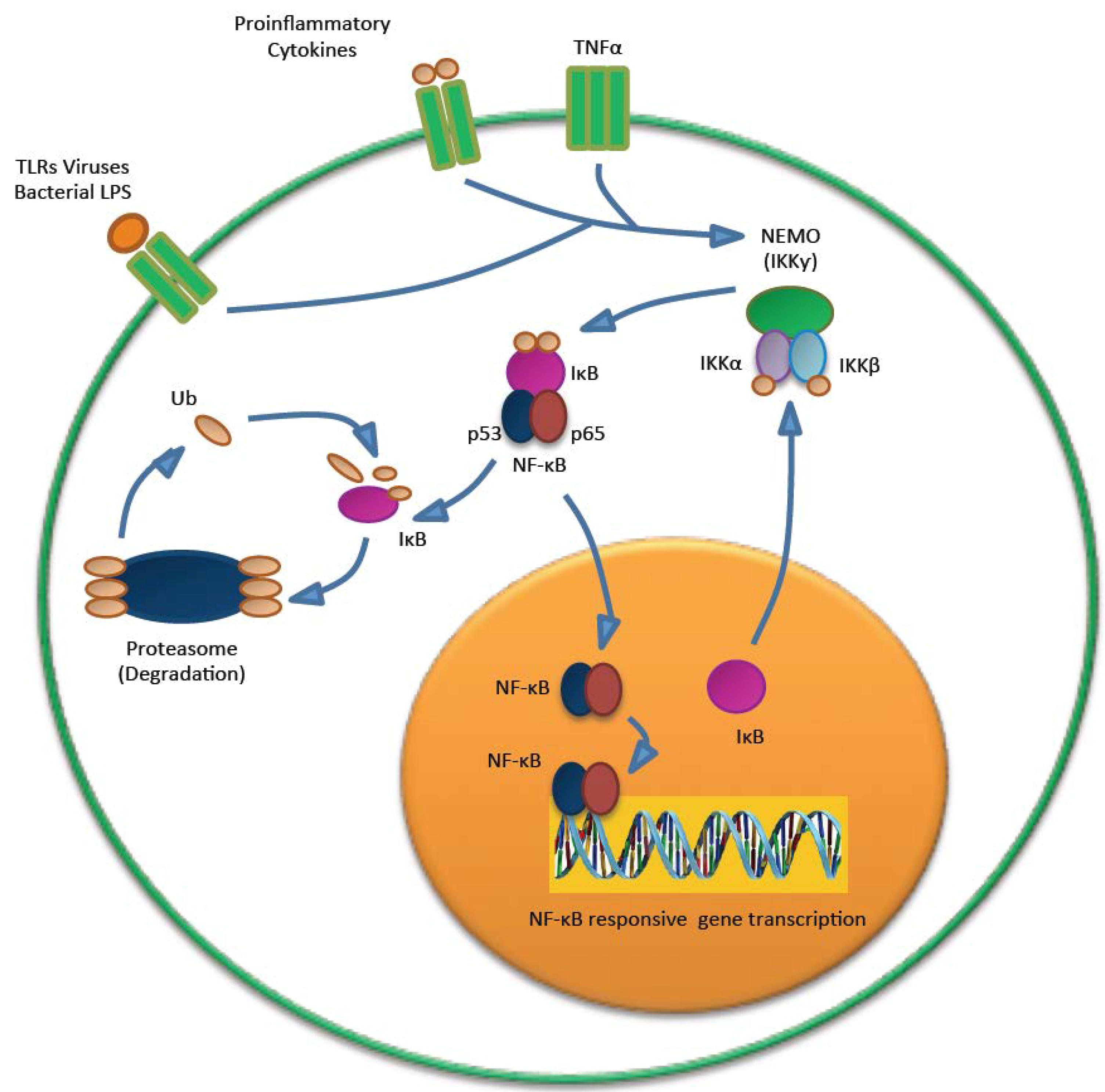
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Molecular Insights into the Most Recently Discovered Human Tumour Virus

Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen targets the NEMO adaptor protein to disrupt inflammatory signaling. - Abstract - Europe PMC
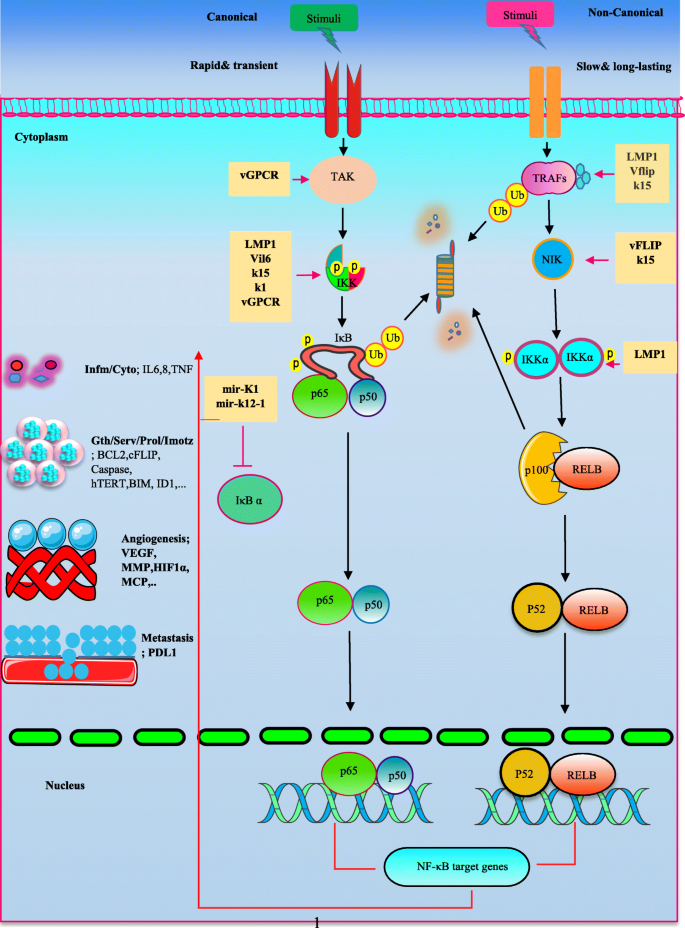
The interplay between EBV and KSHV viral products and NF-κB pathway in oncogenesis | Infectious Agents and Cancer | Full Text

Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Targets the NEMO Adaptor Protein To Disrupt Inflammatory Signaling | Journal of Virology

Ubiquitous Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Causative Agent of the Rare Merkel Cell Carcinoma | SpringerLink
![PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/29b5c89417b4ce10560da7d431ce9b0fdc05503b/33-Figure1.1-1.png)
PDF] Understanding the role of Merkel cell polyomavirus oncoproteins in the cellular transformation of mammalian Merkel cells | Semantic Scholar
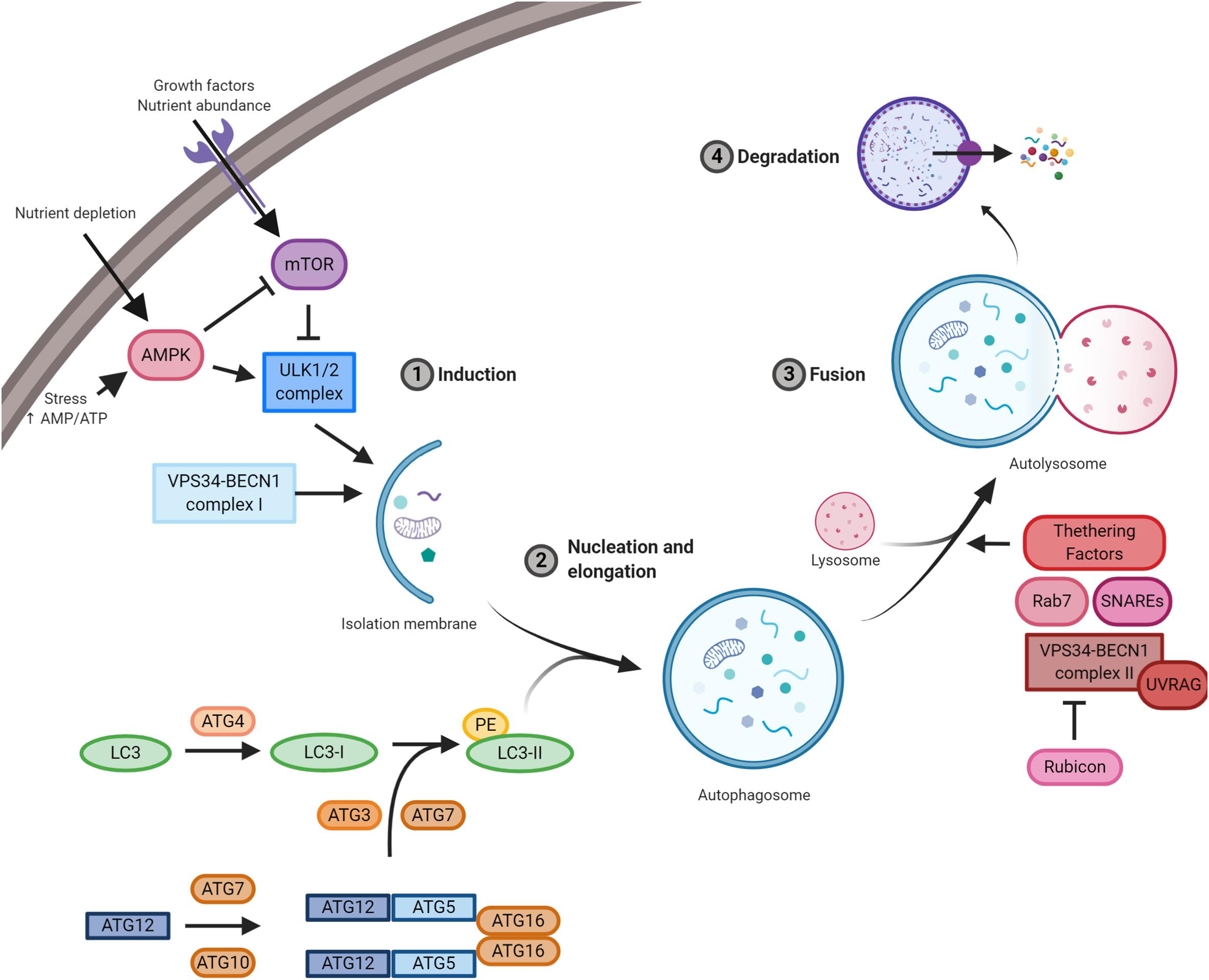
Frontiers | Regulation of Autophagy in Cells Infected With Oncogenic Human Viruses and Its Impact on Cancer Development

Frontiers | Functional Domains of the Early Proteins and Experimental and Epidemiological Studies Suggest a Role for the Novel Human Polyomaviruses in Cancer